



Next: DLVQ in SNNS
Up: Dynamic Learning Vector
Previous: Dynamic Learning Vector
The idea of this algorithm is to find a natural grouping in a set of
data ([SK92], [DH73]. Every data vector is associated
with a point in a d-dimensional data space. The hope is that the
vectors 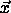 of the same class form a cloud or a cluster in data
space. The algorithm presupposes that the vectors
of the same class form a cloud or a cluster in data
space. The algorithm presupposes that the vectors 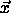 belonging
to the same class
belonging
to the same class 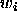 are distributed normally with a mean vector
are distributed normally with a mean vector
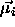 , and that all input vectors are normalized. To
classify a feature vector
, and that all input vectors are normalized. To
classify a feature vector 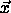 measure the Euclidian distance
measure the Euclidian distance
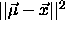 from
from 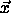 to all other mean vectors
to all other mean vectors
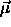 and assign
and assign 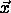 to the class of the nearest mean. But
what happens if a pattern
to the class of the nearest mean. But
what happens if a pattern 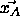 of class
of class 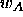 is assigned
to a wrong class
is assigned
to a wrong class 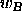 ? Then for this wrong classified pattern the
two mean vectors
? Then for this wrong classified pattern the
two mean vectors 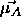 and
and 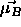 are moved or
trained in the following way:
are moved or
trained in the following way:
- The reference vector
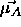 which the wrong classified
pattern belongs to, and which is the nearest neighbor to this pattern,
is moved a little bit towards this pattern.
which the wrong classified
pattern belongs to, and which is the nearest neighbor to this pattern,
is moved a little bit towards this pattern.
- The mean vector
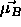 , to which a pattern of class
, to which a pattern of class 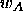 is
assigned wrongly, is moved away from it.
is
assigned wrongly, is moved away from it.
The vectors are moved using the rule:

where 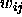 is the weight
is the weight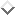 between the output
between the output 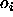 of a input unit i and a output unit j.
of a input unit i and a output unit j.
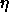 is the learning parameter. By choosing it less or greater than
zero, the direction of movement of a vector can be influenced.
is the learning parameter. By choosing it less or greater than
zero, the direction of movement of a vector can be influenced.
The DLVQ algorithm works in the following way:
- Load the (normalized) training data, and calculate for every class the
mean vector
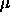 . Initialize the net with these vectors. This means:
Generate a unit for every class and initialize its weights with the
corresponding values.
. Initialize the net with these vectors. This means:
Generate a unit for every class and initialize its weights with the
corresponding values.
- Now try to associate every pattern in the training set with a
reference vector. If a trainings vector
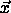 of a class
of a class 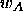 is assigned to a class
is assigned to a class 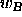 then do the following:
then do the following:
- Move the vector
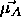 which is nearest to
which is nearest to 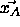 in its direction.
in its direction.
- Move the mean vector
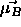 , to which
, to which 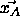 is falsely assigned to away from it.
is falsely assigned to away from it.
Repeat this procedure until the number of correctly classified vectors
no longer increases.
- Now calculate, from the vectors of a class
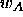 associated
with a wrong class
associated
with a wrong class 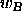 , a new prototype vector
, a new prototype vector 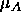 . For every
class, choose one of the new mean vectors and add it to the
net. Return to step 2.
. For every
class, choose one of the new mean vectors and add it to the
net. Return to step 2.




Next: DLVQ in SNNS
Up: Dynamic Learning Vector
Previous: Dynamic Learning Vector
Niels.Mache@informatik.uni-stuttgart.de
Tue Nov 28 10:30:44 MET 1995
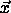 of the same class form a cloud or a cluster in data
space. The algorithm presupposes that the vectors
of the same class form a cloud or a cluster in data
space. The algorithm presupposes that the vectors 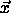 belonging
to the same class
belonging
to the same class 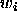 are distributed normally with a mean vector
are distributed normally with a mean vector
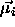 , and that all input vectors are normalized. To
classify a feature vector
, and that all input vectors are normalized. To
classify a feature vector 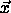 measure the Euclidian distance
measure the Euclidian distance
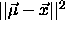 from
from 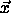 to all other mean vectors
to all other mean vectors
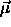 and assign
and assign 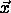 to the class of the nearest mean. But
what happens if a pattern
to the class of the nearest mean. But
what happens if a pattern 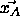 of class
of class 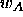 is assigned
to a wrong class
is assigned
to a wrong class 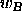 ? Then for this wrong classified pattern the
two mean vectors
? Then for this wrong classified pattern the
two mean vectors 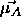 and
and 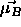 are moved or
trained in the following way:
are moved or
trained in the following way:
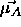 which the wrong classified
pattern belongs to, and which is the nearest neighbor to this pattern,
is moved a little bit towards this pattern.
which the wrong classified
pattern belongs to, and which is the nearest neighbor to this pattern,
is moved a little bit towards this pattern.
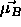 , to which a pattern of class
, to which a pattern of class 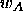 is
assigned wrongly, is moved away from it.
is
assigned wrongly, is moved away from it.

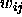 is the weight
is the weight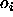 of a input unit i and a output unit j.
of a input unit i and a output unit j.
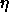 is the learning parameter. By choosing it less or greater than
zero, the direction of movement of a vector can be influenced.
is the learning parameter. By choosing it less or greater than
zero, the direction of movement of a vector can be influenced.
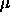 . Initialize the net with these vectors. This means:
Generate a unit for every class and initialize its weights with the
corresponding values.
. Initialize the net with these vectors. This means:
Generate a unit for every class and initialize its weights with the
corresponding values.
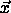 of a class
of a class 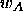 is assigned to a class
is assigned to a class 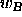 then do the following:
then do the following:
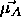 which is nearest to
which is nearest to 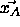 in its direction.
in its direction.
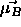 , to which
, to which 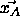 is falsely assigned to away from it.
is falsely assigned to away from it.
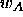 associated
with a wrong class
associated
with a wrong class 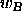 , a new prototype vector
, a new prototype vector 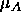 . For every
class, choose one of the new mean vectors and add it to the
net. Return to step 2.
. For every
class, choose one of the new mean vectors and add it to the
net. Return to step 2.