

The human vision system can only distinguish about 30 shades of grey in a monochrome image, but it can distinguish hundreds of different colors shades.
Pseudocoloring is a technique to artificially assign colors to a grey scale. There are various approaches for assigning color to grey-level images. A technique, known as intensity slicing, assigns a shade of color to all grey levels that fall under a specified value and a different shade of color to those grey levels that exceed the specified value. The majority of the techniques perform a grey level to color transformations. The idea is to perform 3 transformations on a particular grey level and feed this to the three color inputs (RGB) of a color monitor. The result is a composite image whose color content depends on the grey level to color transformations.

|
|---|
Basically we want to "play" (alter) the colormap of an image. The two methods are:

Two mapping schemes.
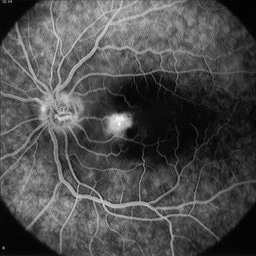
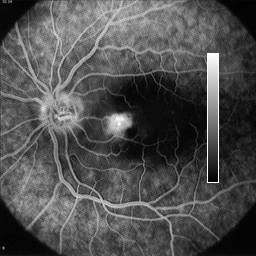
Below is an original grey scale or monochrome image and next to it is the same image but with a grey level ramp inserted in it. This is done so that the colortable can be visualized directly in the image display.
The technique to generate the image with a built-in grey-ramp is very useful to understand how the colors are mapped in the display.
|
|
|---|---|
| a) | b) |
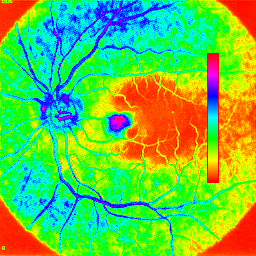
Shown below are two images using two different pseudocolor tables. The image on the left uses the "rainbow" colortable and the one on the right uses the "SApseudo" colortable.
|
|
|---|---|
| a) | b) |